Empowering Inclusivity: Navigating Mobile Accessibility Testing for a User-Friendly Digital Future
According to a WHO report, 15 percent of the global population has some kind of disability. As the digital era progresses, companies should make digital content accessible to every Internet user, including those with disabilities. This is where the accessibility test comes into the limelight. One effective method to conduct mobile app testing and website accessibility testing is using a mobile device lab.
Mobile accessibility testing is a critical step in ensuring that your digital products are user-friendly and inclusive for everyone. Developers should comply with accessibility guidelines during the software/ product development process. The same applies to QA teams, who now have testing for accessibility in software solutions and products. In this article, we will give you insights into important principles of mobile accessibility testing and deliver a step-by-step step to get started.
What is an Accessibility Test?
Testing for accessibility is the assessment of a mobile application or website to confirm that it can be easily used and accessed by end users. Through comprehensive accessibility testing, companies can eradicate design flaws in their mobile app or website that act as hurdles preventing folks, particularly individuals with disabilities, from meaningfully utilizing them.
Accessibility testing is considered a section of usability testing. The acronym for accessibility is A11Y, with the number 11 signifying the no. of letters discarded.
The W3C (World Wide Web Consortium) has formed the following accessibility test guidelines:
W3C (World Wide Web Consortium) has defined 3 conformance levels – A, AA, & AAA that companies can utilize in their software development & testing life cycle.
What is Mobile Accessibility Testing?
It ensures websites and applications are accessible to folks with disabilities. This counts multiple cognitive, physical, visual, and auditory disabilities.
According to W3C “Mobile accessibility” refers to making apps and sites extremely accessible to folks with disabilities when they are using diverse devices. WAI’s work in this zone addresses accessibility concerns of persons using a comprehensive range of devices to interact with the web: tablets, smartphones, TVs, and more.
What are some instances of accessibility testing?
Instances of accessibility testing include keyboard evaluation of text sizing, User Interface structure, accessibility review, content scaling, style disablement, and accessibility testing tools utilization for enhanced efficiency and accuracy.
What are some common accessibility guidelines for websites and mobile apps?
Common accessibility guidelines comprise the WCAG (Web Content Accessibility Guidelines). Such guidelines proffer definite criteria for making web content accessible, comprising mobile apps and sites. WCAG is well-organized into 4 principles: POUR (Perceivable, Operable, Understandable, and robust).
What are some critical areas to test for mobile accessibility?
Some of the critical areas to test comprise:
Categories of Accessibility Testing
In SDLC (Software Development Life Cycle), you can conduct Accessibility Tests in automated and manual approaches. There are two forms of Accessibility testing:
Manual Accessibility Testing
This form of testing is a method of using an odd arrangement of assistive technologies, keyboard interfaces, and browser plugins to test web apps and website accessibility. It assists in detecting problems that cannot be identified programmatically. But, running accessibility testing is a time-consuming procedure and is prone to manual errors.
Automated Accessibility Testing
This kind of accessibility testing is an extremely effective method of web app testing. QA specialists can leverage Accessibility testing tools for testing various web apps and websites. It helps lessen test implementation time, is lucrative, focuses on core areas that require attention, and makes the complete procedure faster.
Why is Mobile Accessibility Testing Significant?
Steps to Test Mobile Accessibility:
Accessibility tests utilize a range of methodologies, including automated and manual testing. It is an ongoing procedure that frequently tests and assesses an app or website’s accessibility.
General steps for running accessibility test:
Review accessibility guidelines & standards
Know the accessibility guidelines and standards for the environment, product, or service being tested, such as the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) or Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG) guidelines.
Arrange the test environment
This phase includes setting up the test environment and tools, such as assistive technologies and testing software, for use during the test process.
Use Accessibility Testing Tools
There are frequent accessibility test tools accessible that can help you find issues with your website or mobile application. Some of the most common and popular tools comprise:
Conduct Manual test
Use manual test methods, such as navigation with a keyboard, and methods, such as screen reader testing, to test the environments, products, and services.
Perform automated testing
Implement automated testing tools to scan the mobile app or website for accessibility problems, like missing alt text or poor color difference.
Testing with Real Users
Involving users with disabilities in the testing procedure is beneficial. They can give real-world feedback on the accessibility of your website or mobile application.
Evaluate the outputs
Analyze the test procedure results and find accessibility issues that require immediate addressing.
Address the problems
Make modifications to your software product to fix the accessibility issues detected during testing.
Retesting
Retesting the software product to ensure that the accessibility problems are no longer present and that the modifications don’t introduce new accessibility problems.
Document and report
Document the test procedure and the outcomes and report the findings to stakeholders.
How to perform Accessibility Testing using LambdaTest?
LambdaTest is an AI-powered test orchestration and execution platform that lets you run manual and automated tests at scale with over 3000+ real devices, browsers, and OS combinations. It also allows you to test the accessibility of web apps and sites using Speech Viewer and Screen Reader using Non-Visual Desktop Access (NVDA) for macOS and Windows platforms. In this section, let us look at how to test the accessibility of your site on the LambdaTest platform.
 3. Enter a test URL and select OS, VERSION, and RESOLUTION. After that, click on START.
3. Enter a test URL and select OS, VERSION, and RESOLUTION. After that, click on START. 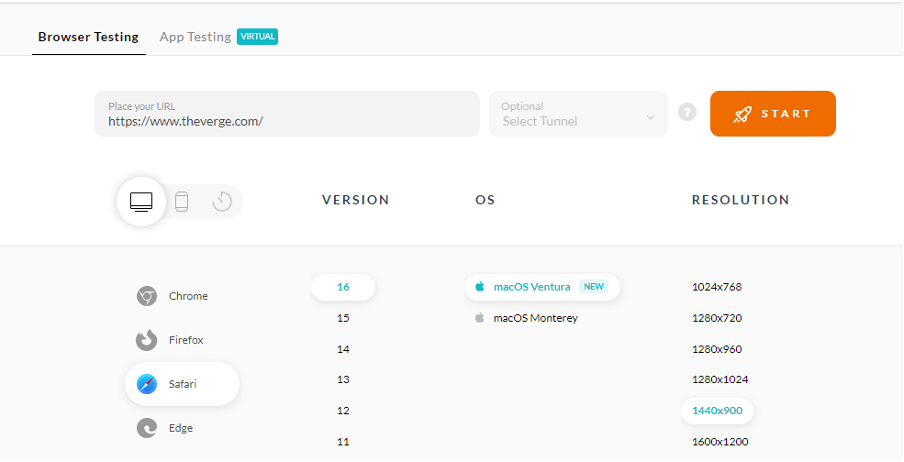 4. After a cloud-centric machine launches, click on the Settings icon & select Accessibility
4. After a cloud-centric machine launches, click on the Settings icon & select Accessibility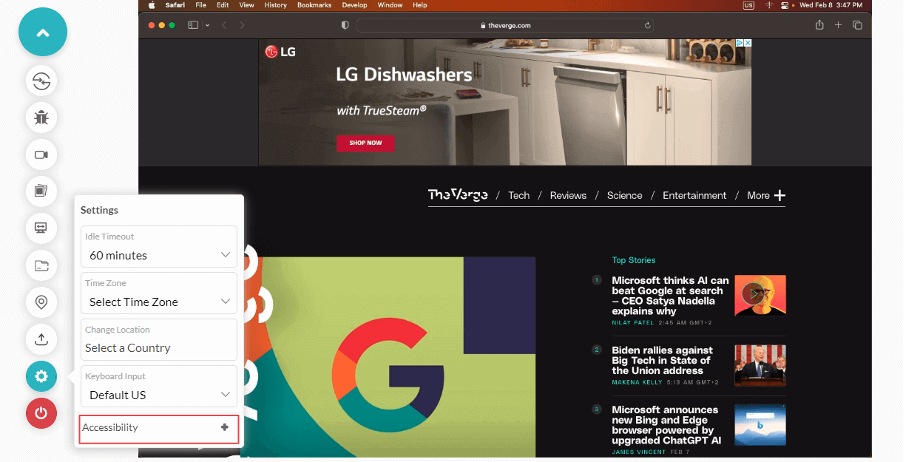 5. Choose the checkbox that denotes Screen Reader, and you will obtain a verbal description of your web page via VoiceOver.
5. Choose the checkbox that denotes Screen Reader, and you will obtain a verbal description of your web page via VoiceOver.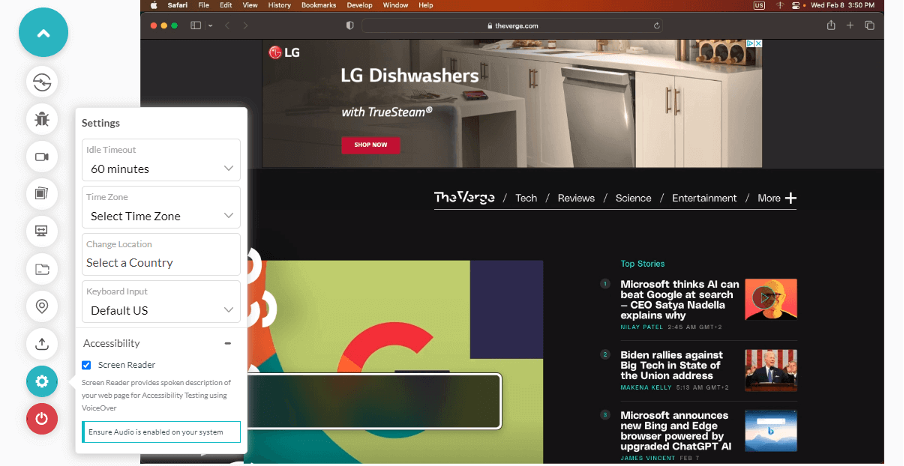 Advantages of Accessibility Testing
Advantages of Accessibility Testing
Accessibility testing can help companies enhance user experience, meet legal requirements, increase market reach, improve Search Engine Optimization, save costs, enhance brand reputation, and follow user-centered web design principles.
Besides the obvious reasons why accessibility testing must be a part of any business, here are some exceptional advantages as to why you must utilize them in your STLC (Software Testing Life Cycle). These advantages include:
In a nutshell, mobile accessibility testing is a crucial facet of creating inclusive digital experiences. By following accessibility guidelines like Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG), involving real users, utilizing testing tools, and staying updated with best practices, you can certify that your website or mobile app is accessible to everyone. Remember that accessibility benefits every user and makes your web product compliant with legal requirements and more user-friendly.
Jumpstart your ride toward greater inclusivity now!

